The level of health literacy of secondary school students in Slovenia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17532/jhsci.2021.1272Keywords:
Health literacy, adolescents, rural environment, nursingAbstract
Introduction: Health literacy of secondary school students is particularly important as they are exposed to higher health risk. Therefore, the aim of the study is to determine the level of basic health literacy, critical and mental health literacy, and numeracy of Slovenian secondary school nursing students using a cross-sectional comparative method.
Methods: The questionnaire measuring the level of basic numerical, critical, and mental health literacy was completed by 249 secondary school students, divided into a group of secondary school students attending a nursing program and students of others similar secondary schools such as economic technician, chemical technician and preschool education.
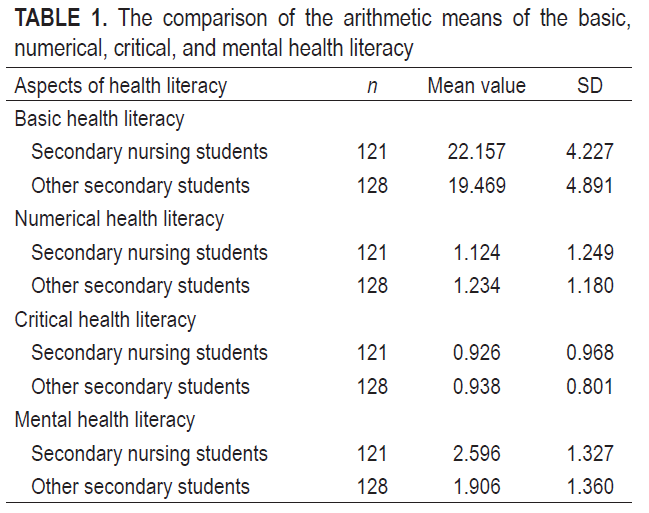
Results: Secondary nursing students were found to have statistically significantly higher levels of basic and mental health literacy than their peers, rather than numerical and critical health literacy. In addition, the results show that there is no statistically significant difference in the level of health literacy between the groups of secondary school students in relation to the environment (rural/urban area).
Conclusion: Numerical and critical health literacy should be systematically developed in nursing schools, and at least the basic aspects of health literacy should be introduced in all secondary school curricula.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Monika Sadar, Karmen Erjavec

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










