Job satisfaction among nurses in Canton Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17532/jhsci.2025.2967Keywords:
Job satisfaction, Nurses, Job satisfaction survey, HealthcareAbstract
Introduction: Job satisfaction of nurses is an important indicator of the safety and quality of healthcare and professional efficiency. Its level directly affects employee motivation and patient satisfaction. It is determined by financial and organizational factors, job content, and interpersonal relationships. The aim of this research is to assess the level of job satisfaction among nurses in public health institutions in Canton Sarajevo and to identify the factors that shape job satisfaction in this professional group to the greatest extent.
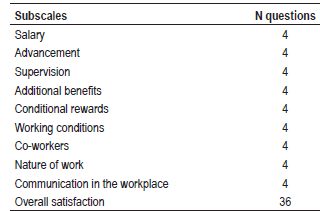
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted from May to June 2025 on a sample of 504 nurses. The job satisfaction survey questionnaire was used to collect data. The overall score was classified into dissatisfaction, ambivalence, and satisfaction, and the associations with sociodemographic and work characteristics were assessed with the Chi-square test (p < 0.05).
Results: Almost half of the respondents were dissatisfied with their job (47.6%), whereas 38.5% reported ambivalent attitudes and 13.9% were satisfied. Job satisfaction was significantly associated with length of service, compatibility of work with education, management function, working hours, type of institution, psychological job demands, and income level (p < 0.05). No statistically significant associations were found with gender, age, marital status, number of children, level of education, or job changes (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Job satisfaction among nurses stems from job content and relationships, and dissatisfaction from financial and organizational factors. Priority measures include fair valuation of work, clear reward systems, and development support to improve healthcare outcomes.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mufida Zukić, Elma Sokić Begović, Amela Salihović, Mirad Hujdur, Anes Jogunčić, Jasna Husejinbegović-Musić, Jasmina Mahmutović

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










